Get ready to embark on a tech-infused journey transforming the healthcare scene. Virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) are creating a serious buzz everywhere right now – and that effect is also being felt in healthcare. These immersive technologies are more than just futuristic gadgets or temporary trends in healthcare. They’re in place and ready to redefine medicine and bring a whole new dimension to healthcare.
In this article, we’ll review how AR, VR and MR are becoming dynamic allies in healthcare through applications in surgery, training and patient care. We also discuss benefits like improved outcomes and cost-effectiveness, address challenges like affordability and offer insights into future trends that offer an exciting dose of innovation.
Understanding AR, VR and MR in Healthcare
Getting used to the evolving techscape and language that goes with it can be confusing. To keep it simple, here’s a quick breakdown of the fundamental differences between AR vs. VR vs. MR.
Augmented reality overlays digital information into the real world. The most well-known application of this was Pokémon GO from 2016, where people could walk with their phones chasing the virtual Pokémon through actual reality. AR seamlessly blends digital aspects into real-world information. Virtual reality immerses the user in a fully computer-generated environment, whereas mixed reality is a seamless blend between the real and virtual worlds.
Immersive technology in healthcare isn’t as new as you might think – it dates back to the 1990s. VR found early applications in medical training, creating simulated environments for skill development. AR gained traction in the early 2000s, particularly in surgical procedures and medical education, offering real-time data overlays. AR, VR and MR each continue to reshape healthcare in unique ways, with the promise of improving training methods, enhancing the patient experience and contributing to more effective medical practices.
What Is Augmented Reality in Healthcare?
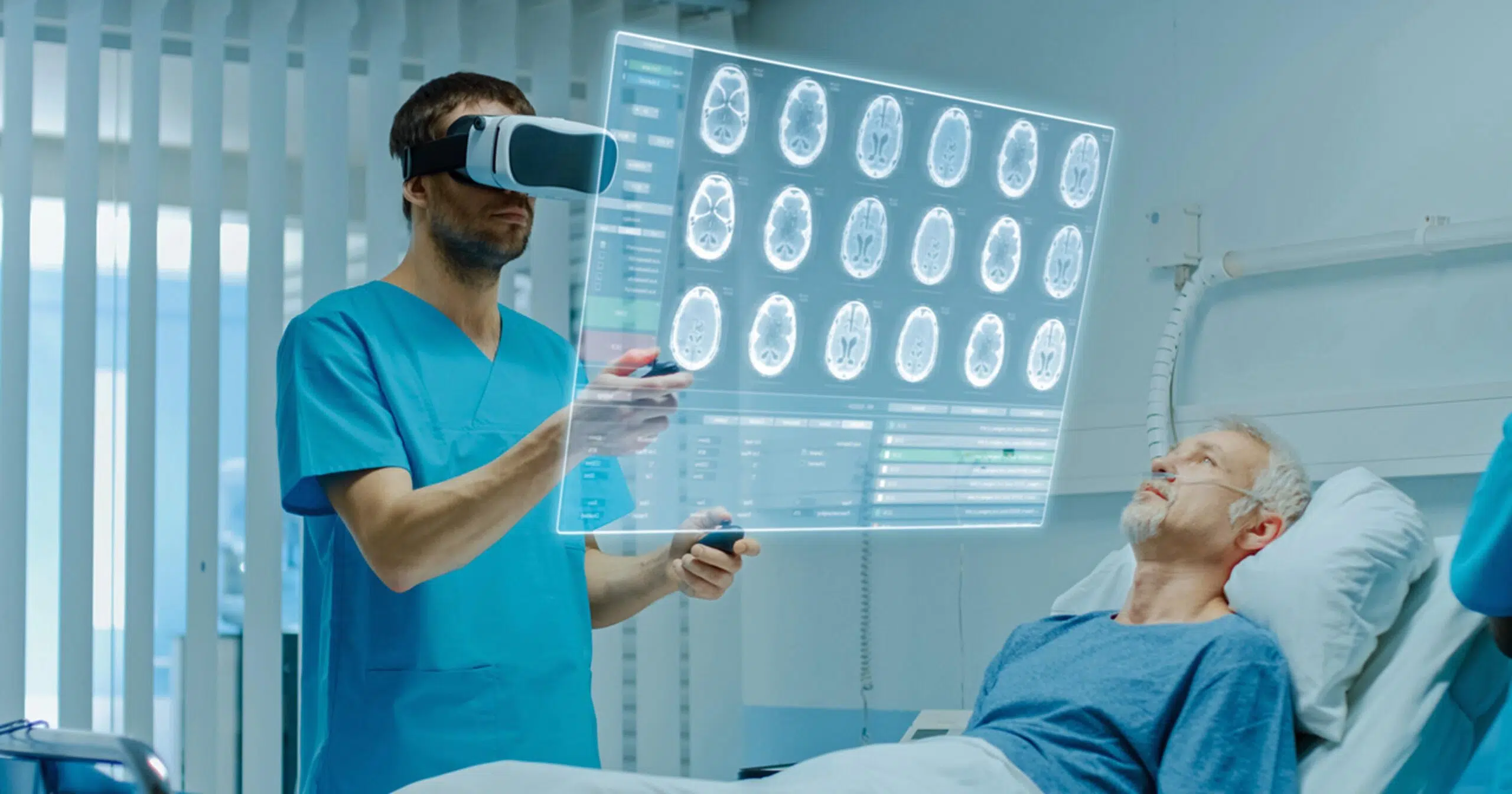
AR overlays digital information onto the real-world environment, enhancing the user’s perception by adding virtual elements. In healthcare, AR enhances training by providing interactive learning experiences and aids surgery through precise preoperative planning and real-time guidance. For example, HCPs can use AR in perioperative planning to generate a three-dimensional (3D) representation of hepatic and biliary structures. AR then overlays these virtual images into the surgical field to assist surgeons in better visualizing intrahepatic structures, facilitating greater precision and enhancing clinical outcomes.
What Is Virtual Reality in Healthcare?
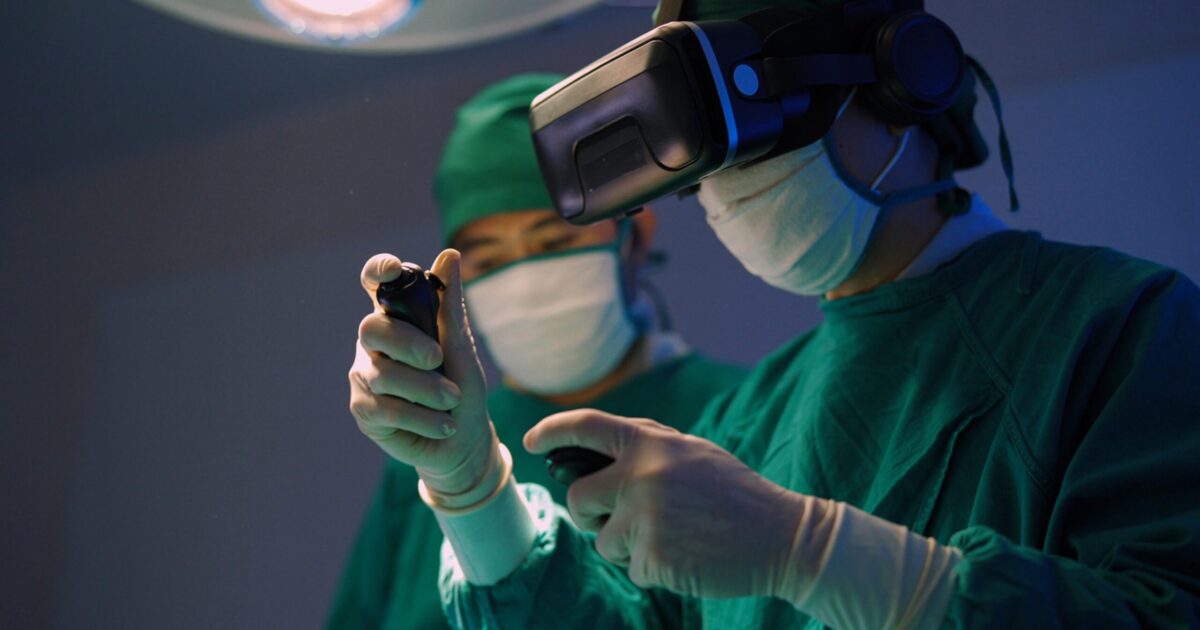
VR immerses users in a fully computer-generated environment, isolating them from the real world. VR in healthcare is used for medical training simulations, therapeutic application and perioperative planning. Primarily used in training, it lets professionals practice procedures in a risk-free environment. VR also allows patients to visualize medical concepts in patient education, aiding informed decision-making. Therapeutically, it’s effective for exposure therapy and mental health treatments. In surgery, VR enhances perioperative planning by visualizing anatomy in 3D. VR in healthcare isn’t just tech – it’s transforming training, empowering patients and optimizing therapies.
What Is Mixed Reality in Healthcare?
MR merges the real and virtual worlds, allowing digital and physical elements to interact. In healthcare, MR facilitates immersive experiences for surgical planning, medical training and patient education.
MR in healthcare is a cutting-edge technology that seamlessly combines elements of both VR and AR. It creates an immersive and interactive environment by overlaying digital information into the real-world setting, allowing users to interact with both physical and virtual elements simultaneously.
An article published in the Frontiers in Pain Research shows promising results using MR to reduce phantom limb pain in amputees. This process begins by creating a virtual representation of the patient’s missing limb. They’re then immersed in a 3D environment where they can interact with their 3D-generated limb and surrounding area. This has been shown to be a safe and effective way to relieve the neuropathic pain that may come with amputation.
Mixed reality is at the forefront of technological innovation in healthcare, offering a bridge between the physical and virtual realms to improve medical practices, enhance training and elevate the patient experience.
Immersive Technology Applications in Healthcare
The possibilities regarding immersive technologies are ever-expanding in the healthcare realm. The following offers a breakdown of some of the most widely used applications involving immersive technology.
Surgical Efficiency
AR and VR are emerging as indispensable tools, notably in surgical procedures. These tools bring forth a spectrum of benefits for surgeons and patients and are reshaping surgical efficiency. AR is being used in surgical navigation by providing surgeons with real-time guidance through AR overlays, equipping surgeons to receive instantaneous data during procedures. Having an AR overlay assists in precise navigation through complex anatomical structures, offering surgeons enhanced precision.
With the use of VR in education, surgeons are able to engage in realistic virtual simulations, practicing intricate procedures before actual surgery. VR simulations contribute to skill development and increased confidence among surgeons. The simulations enable surgeons to rehearse and refine techniques, reducing the risk of error during actual procedures.
Training and Education
The fusion of VR and MR inspires a transformative shift in medical training and simulations. This immersion into digital realms isn’t merely a technological display but a pivotal force reshaping learning outcomes and skill development for healthcare professionals. VR and MR accelerates skill acquisition, increases confidence and reduces learning curves, among other benefits. Some ways HCPs can use VR and MR in medical training and interactive learning include:
- Realistic Simulations: VR plunges medical trainees into realistic scenarios, replicating surgical procedures, emergencies and complex medical cases, making simulations more effective.
- Hands-On Experience: Trainees gain hands-on experience without real-world consequences, allowing them to refine their skills and decision-making processes in a risk-free VR environment.
- Enhanced Engagement: VR fosters heightened engagement through interactive modules, offering interactivity that traditional methods often lack.
- Real-Time Manipulation: MR takes learning a step further by enabling real-time manipulation of 3D models, enhancing trainees’ understanding by letting them interact with anatomical structures.
- Interactive Anatomy Modules: VR/AR anatomical platforms with 3D modules allow trainees to delve into the intricacies of the human body with unprecedented depth.
- Collaborative Learning: Immersive technology allows trainees to interact with virtual and physical elements, promoting teamwork and communication skills.
Patient Care

AR, VR and MR enhance the patient experience by providing a deeper understanding of medical treatments, leading to informed decision-making. Exposing patients to complex procedures or surgeries through immersive technology reduces anxiety and leads to a holistic patient-centric approach.
HCPs may primarily use AR for patient care in diagnostics and treatment planning, including in the following ways:
- Real-Time Treatment Guidance: AR overlays real-time patient data onto the surgeon’s field of view during procedures, offering precision and real-time guidance.
- Enhanced Visualization: AR provides an augmented view of patient anatomy, aiding HCPs in diagnostics and treatment planning with unparalleled clarity.
- Interactive Patient Data: Patient data becomes interactive and accessible, allowing for collaborative decision-making and comprehensive treatment strategies.
VR is increasingly used to enhance patient engagement in the following ways:
- Visualizing Medical Conditions: VR has become a powerful tool for patient education, enabling individuals to visualize complex medical conditions and treatment plans.
- Immersive Patient Experiences: VR offers immersive experiences that go beyond traditional methods, allowing patients to understand their health journey in a more engaging and interactive manner.
- Personalized Care: VR enables personalized care plans by tailoring educational content to individual patient needs, fostering a deeper understanding and involvement in their healthcare.
Rehabilitation and Therapy
The success stories of immersive technologies in rehabilitation and therapy are well documented. A notable study published in Sensors in 2023 concludes that using VR for rehabilitation with stroke patients, where known tasks are replicated through repetitive functional exercises, has shown positive outcomes by enhancing neuroplastic activation. VR has also demonstrated its efficacy in chronic pain management, with patients reporting reduced pain perception and increased comfort.
Immersive tech has a profound impact on addressing physical health challenges. As technology advances, the potential of personalized and effective rehabilitation strategies appears promising, offering a beacon of hope and tangible results for individuals navigating the recovery journey.
Memory and Cognitive Function
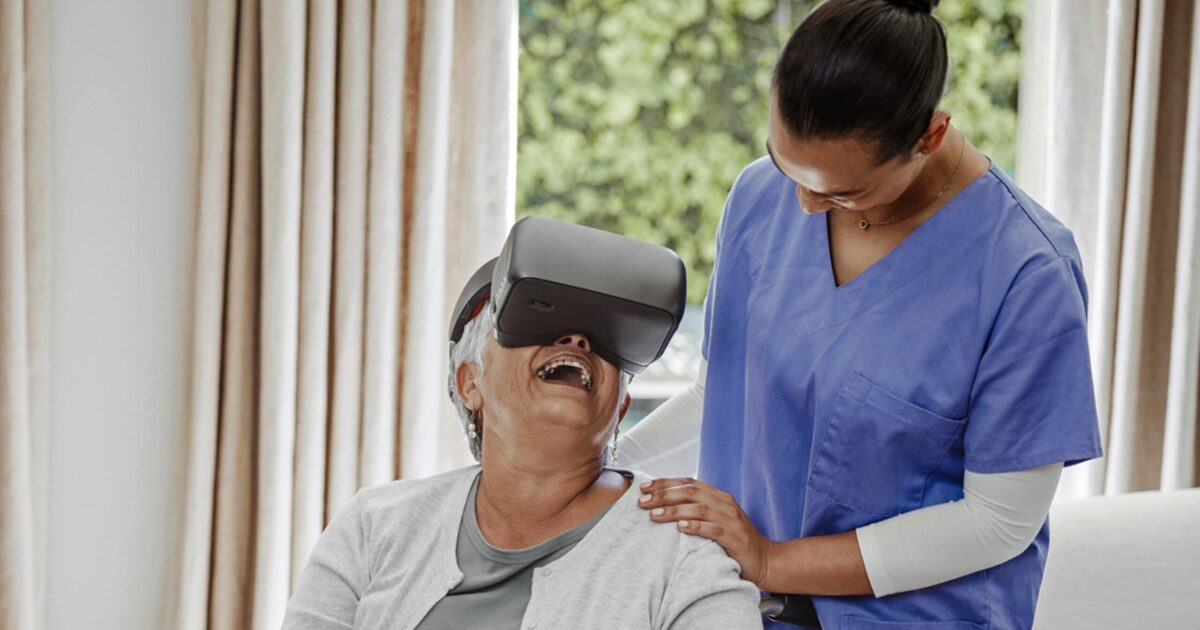

VR is proving to be a game-changer in the realm of memory and cognitive function for seniors facing challenges such as dementia, stroke and multiple sclerosis. The immersive experiences offered by VR have already shown promise in improving memory and cognitive abilities among geriatric patients. This technology provides tailored cognitive training programs, engaging seniors in memory exercises within virtual environments. The impact could be significant, potentially slowing cognitive decline and enhancing memory recall, offering hope for better cognitive health in the aging population.
Another compelling study published in The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association explores the use of MR in Cognitive Therapy for Dementia, showcasing enhanced memory recall and an overall improvement in cognitive function.
Pain Management
VR is transforming pain management by offering a non-pharmacological approach to alleviate both acute and chronic pain. Engaging individuals in immersive virtual environments, VR diminishes pain perception and discomfort, leading to decreased reliance on pharmaceuticals. This innovative method not only provides relief but also addresses the associated anxiety linked with pain. By offering a therapeutic escape, VR becomes a holistic and patient-centered tool, redefining how we approach and treat pain in a more comprehensive and less medicated manner.
Benefits and Challenges of Immersive Technologies in Healthcare
| Benefits | Challenges |
Improved Accuracy and Precision:
Enhanced Training and Skill Acquisition:
Better Patient Engagement and Education:
Cost-effectiveness and Efficiency Improvements:
|
Technological Barriers and Limitations:
Accessibility:
Affordability Issues:
Ethical Considerations:
Data Security:
|
Potential Future of Augmented, Virtual and Mixed Reality in Healthcare
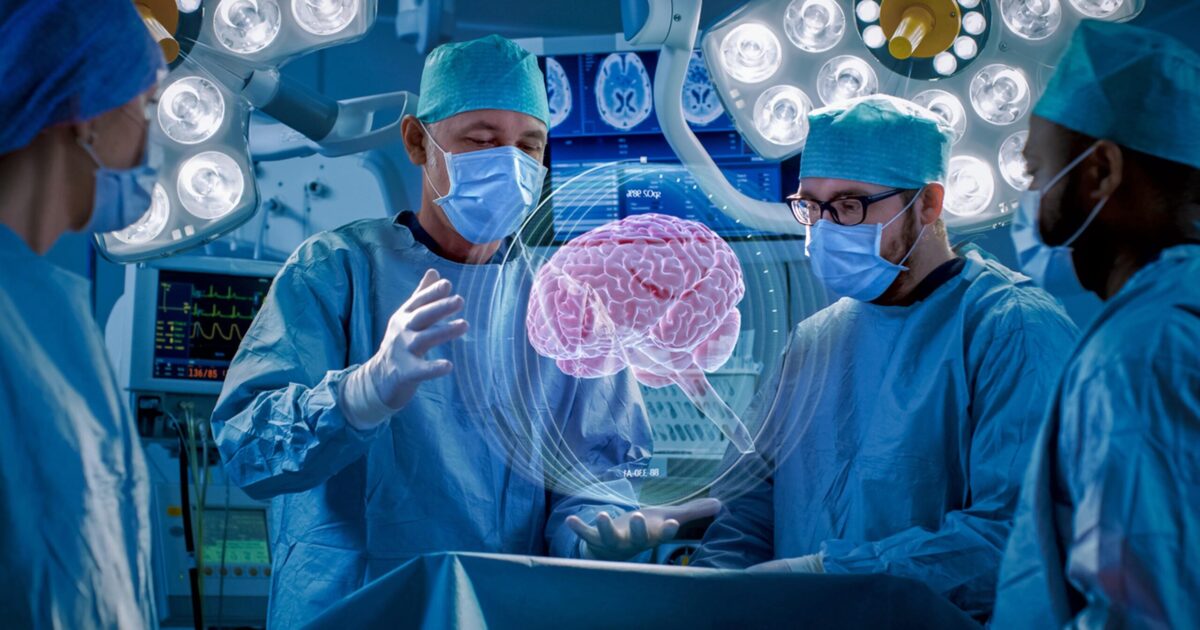
As we peer into the future of healthcare, AR, VR and MR are poised to redefine the industry. Emerging trends indicate a surge in telemedicine applications, enhanced medical training modules and expanded diagnostic and therapeutic uses. Notable predictions foresee seamless integration of AR, VR and MR into routine medical practices, offering more personalized, efficient and patient-centric care.
The potential impact on global healthcare practices is monumental. From improving accessibility to specialized medical expertise through AR-driven telemedicine to revolutionizing surgical procedures with VR simulations, these technologies can bridge healthcare gaps around the world. As we adapt to a new era of healthcare, the integration of AR, VR and MR is becoming an established trend that likely won’t fade due to the overarching need to deliver optimal patient care.
The continuous evolution of immersive technologies makes staying current a dynamic necessity. Healthcare professionals are encouraged to explore and integrate these innovations into their practices, ushering in a future that redefines the boundaries of healthcare and elevates patient outcomes to new heights. Embrace the evolution, consider the possibilities and stay informed on the ever-changing landscape of healthcare technologies.
Stay ahead of the latest trends with the help of Vivian Health. Head to our website to learn the Top 5 Healthcare Trends Impacting Nurse Practitioners in 2024 while searching for your next staff or travel nursing job or allied health role today.









