Within the diverse world of nursing specialties, your career choices are as varied as your patients. Unlike other healthcare fields, nurses can easily transition between specialties with the same degree and minimal extra training. This flexibility is a major draw and keeps nurses engaged, so if you’re craving a change, explore the many opportunities available. While each specialty has unique demands, transferable nursing skills make transitioning between them easy. Let’s explore seven nursing specialties, examining the skills and knowledge each requires and the pathways that connect them.
7 Easily Transferable Nursing Specialties
1. Med-Surg Nursing: The Foundation for Transitioning
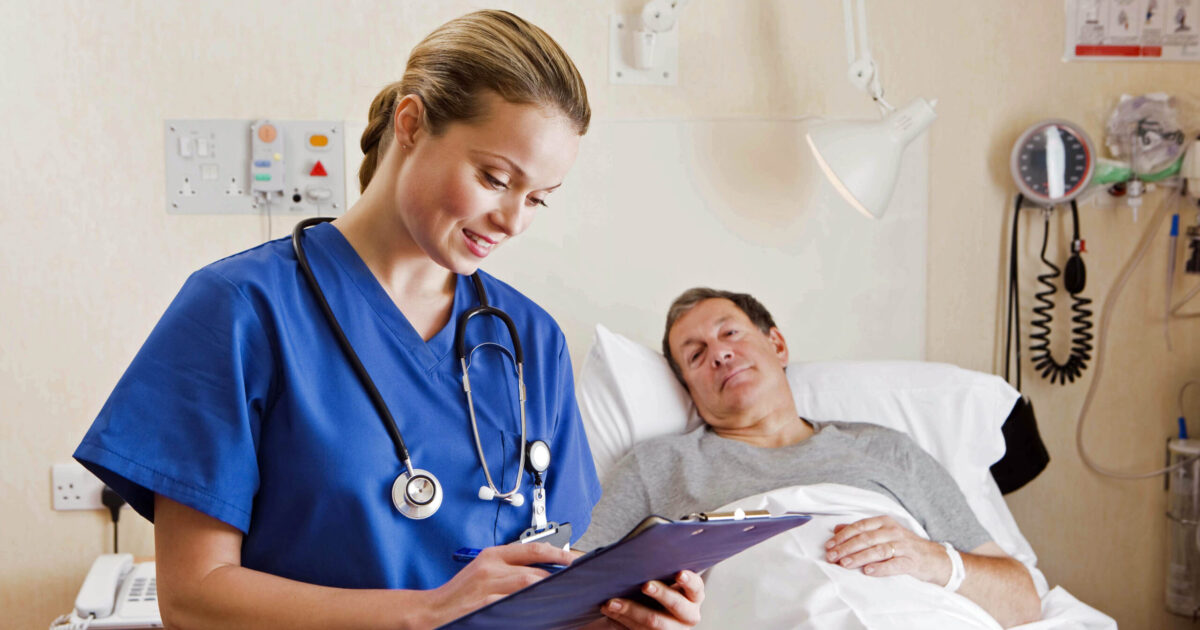

Med-Surg nurses typically work in a hospital setting, caring for acutely ill adult patients. Med-Surg nursing is one of the most popular specialties for new and experienced nurses to excel in and the most versatile.
Recommended Certifications
Transferable Skills and Knowledge
- Total patient care
- Comprehensive assessment and monitoring
- Medication administration and education
- Wound management and infection control
- Pain assessment and management
- Mobility assistance and rehabilitation
- Critical thinking and clinical judgment
- Cultural sensitivity and individualized care
- Accurate documentation for continuity of care
Transition Opportunities
- Long-Term Care or Rehabilitation Facilities: While there may be some differences in care delivery, many of the skills learned in med-surg nursing are applicable in these settings.
- Telemetry/Step-down Units: These units provide care for patients who require close monitoring but don’t need intensive care. Med-Surg nurses can transition to telemetry or step-down units relatively seamlessly due to their familiarity with monitoring equipment and general patient care.
- Home Health or Palliative Care: Med-Surg nurses who enjoy patient education and care coordination may find these roles fulfilling with minimal additional training.
2. Intensive Care Unit Nursing: The Critical Foundation
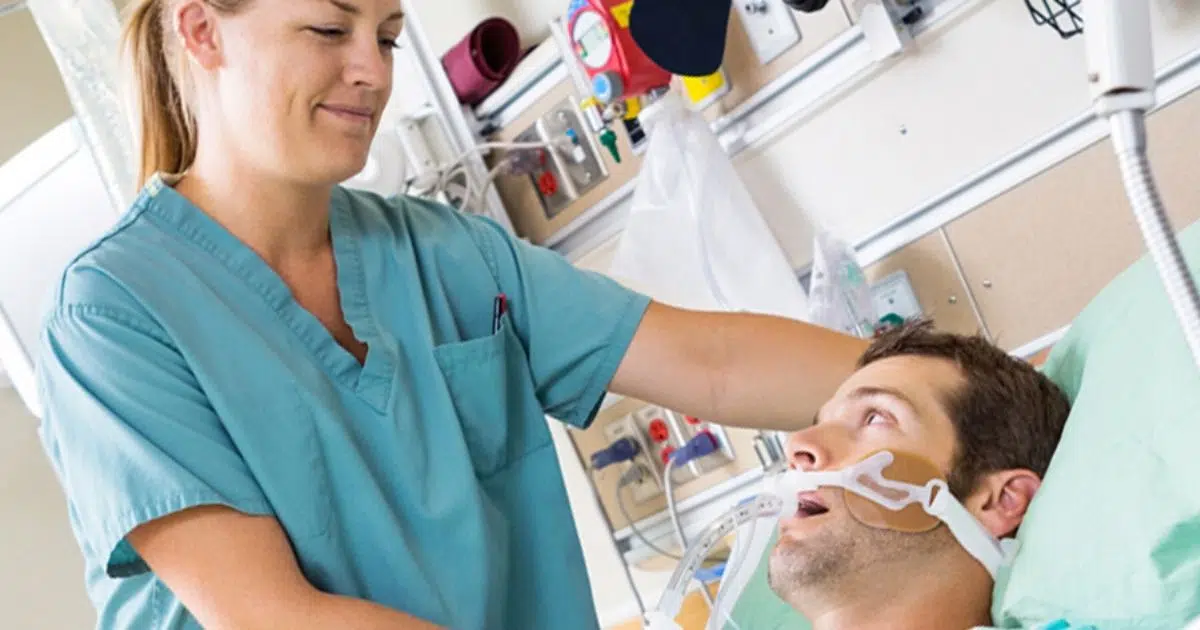
Intensive care unit (ICU) nurses provide specialized care to critically ill patients in a hospital setting. ICU nurses have expertise in critical care and ensure patients receive the highest level of care to optimize outcomes in life-threatening situations.
Recommended Certifications
- Certification in Acute/Critical Care Nursing
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS)
- Basic Life Support (BLS)
Transferable Skills and Knowledge
- Advanced patient assessment
- Hemodynamic monitoring
- Ventilator management
- Advanced medication administration and knowledge
- Critical thinking and decision-making
- Multidisciplinary collaboration
- Crisis management
- Patient advocacy
- Family support and education
- End-of-life care
Transition Opportunities
- Emergency Department (ED): The fast-paced ED environment is familiar to ICU nurses, who are accustomed to making rapid assessments and decisions in high-stress situations. Their experience managing critically ill patients makes them valuable assets in ED settings.
- Critical Care Transport or Flight Nurse: ICU nurses are well-equipped to provide care during patient transfers between healthcare facilities, in ambulances or by air. Their experience managing unstable patients makes them ideal candidates for critical care transport roles. Because ICU skills are directly applicable to the high-acuity medical transport environment, the transition is smoother and requires less additional training compared to nurses from other specialties.
- Clinical Education or Staff Development: Transitioning to roles in education allows ICU nurses to share their expertise and contribute to the professional development of other nurses without requiring extensive clinical retraining.
3. Emergency Nursing: The Frontline Response
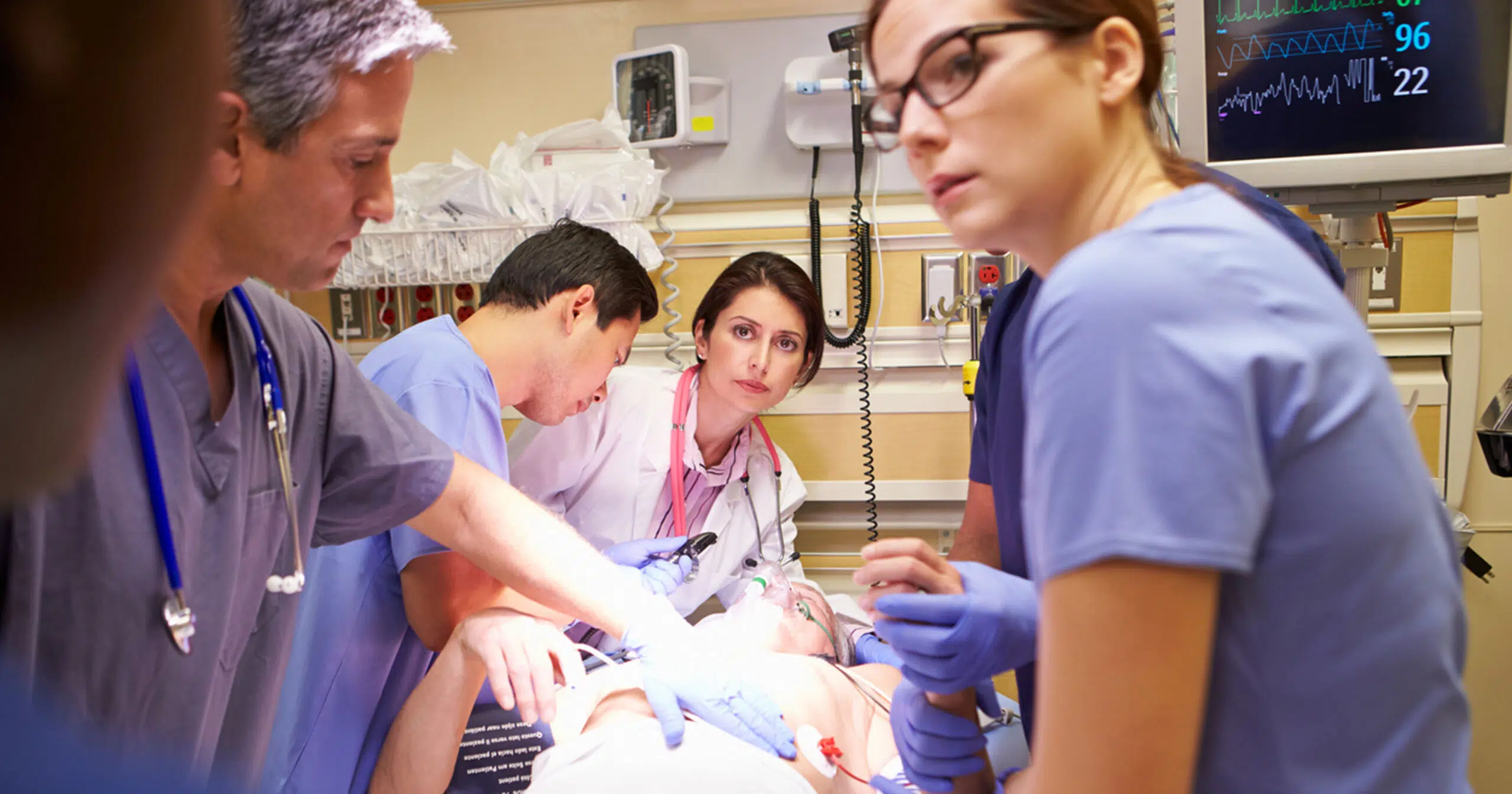
Emergency nursing is a dynamic and fast-paced specialty that focuses on providing immediate care to patients with acute illnesses or injuries. Emergency nurses assess, triage and stabilize patients quickly, often in high-pressure environments such as emergency departments. They play a crucial role in saving lives, managing emergencies and providing compassionate care to patients and their families during times of crisis.
Recommended Certifications
- Certified Emergency Nurse
- Basic Life Support (BLS)
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS)
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS)
- Trauma Nursing Core Course (TNCC)
Transferable Skills and Knowledge
- Proficiency in rapid patient assessment, triage and stabilization
- Ability to prioritize patient needs swiftly and effectively
- Skilled in managing critically ill patients in critical care settings
- Aptitude for immediate interventions in trauma centers
Transition Opportunities
- Occupational Health Nursing: Emergency room (ER) nurses can utilize their expertise in acute care management to promote workplace safety, provide employee health screenings and offer health education programs within corporate or industrial settings.
- Rapid Response Nursing: With rapid assessment skills and a calm demeanor under pressure, ER nurses excel in facilitating timely interventions to ensure patient safety.
- Telehealth Nursing: ER nurses can leverage their assessment and triage skills to provide remote patient care, conduct virtual consultations and offer health advice through telecommunication platforms.
4. Pediatric Nursing: The Compassionate Caregiver
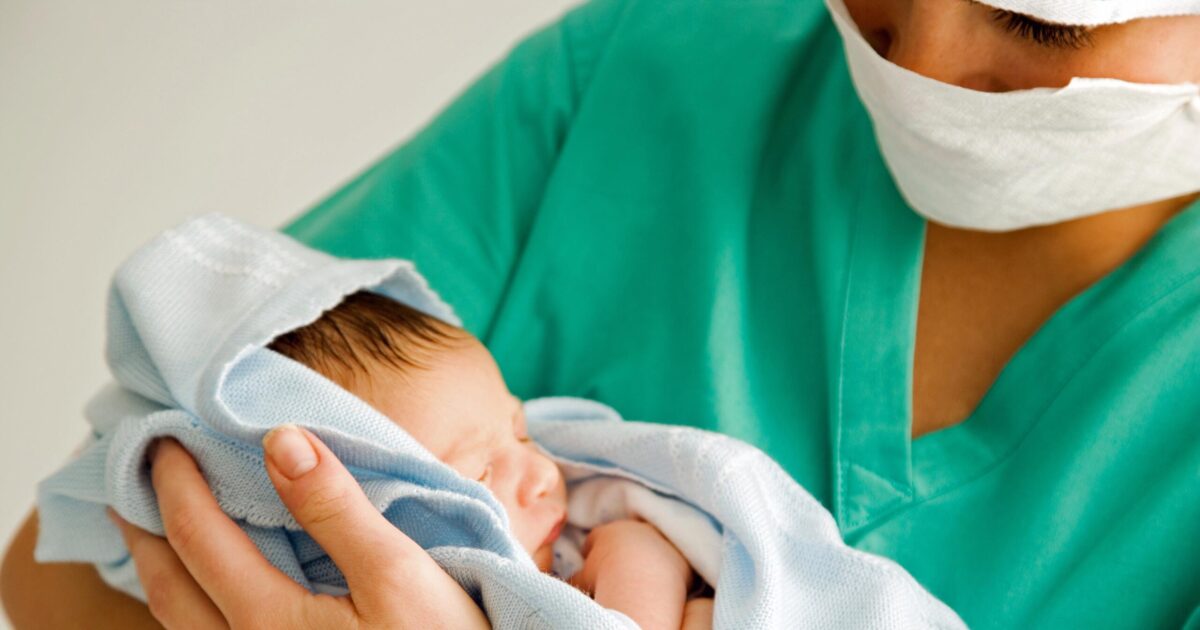

Pediatric nurses specialize in delivering care to infants, children and adolescents, working across diverse healthcare settings such as hospitals, clinics, pediatricians’ offices and schools. Their focus extends beyond physical health, encompassing emotional and developmental support to ensure holistic well-being for young patients.
Recommended Certifications
Transferable Skills and Knowledge
- Pediatric assessment
- Family-centered care
- Pediatric medication administration
- Developmental support
- Pediatric procedures
- Pediatric emergency response
Transition Opportunities
- Pediatric Intensive Care: Skills in pediatric assessment, communication and family-centered care are transferable in providing specialized care to critically ill pediatric patients in intensive care settings.
- Pediatric Oncology: Expertise in pediatric assessment and communication is transferable to pediatric oncology, where nurses provide specialized care and supportive services to children with cancer and their families.
- Pediatric ED: Skills in pediatric assessment, developmental support and emergency response are transferable in providing specialized care to pediatric patients in emergency settings.
5. Obstetric Nursing: The Maternal Advocate
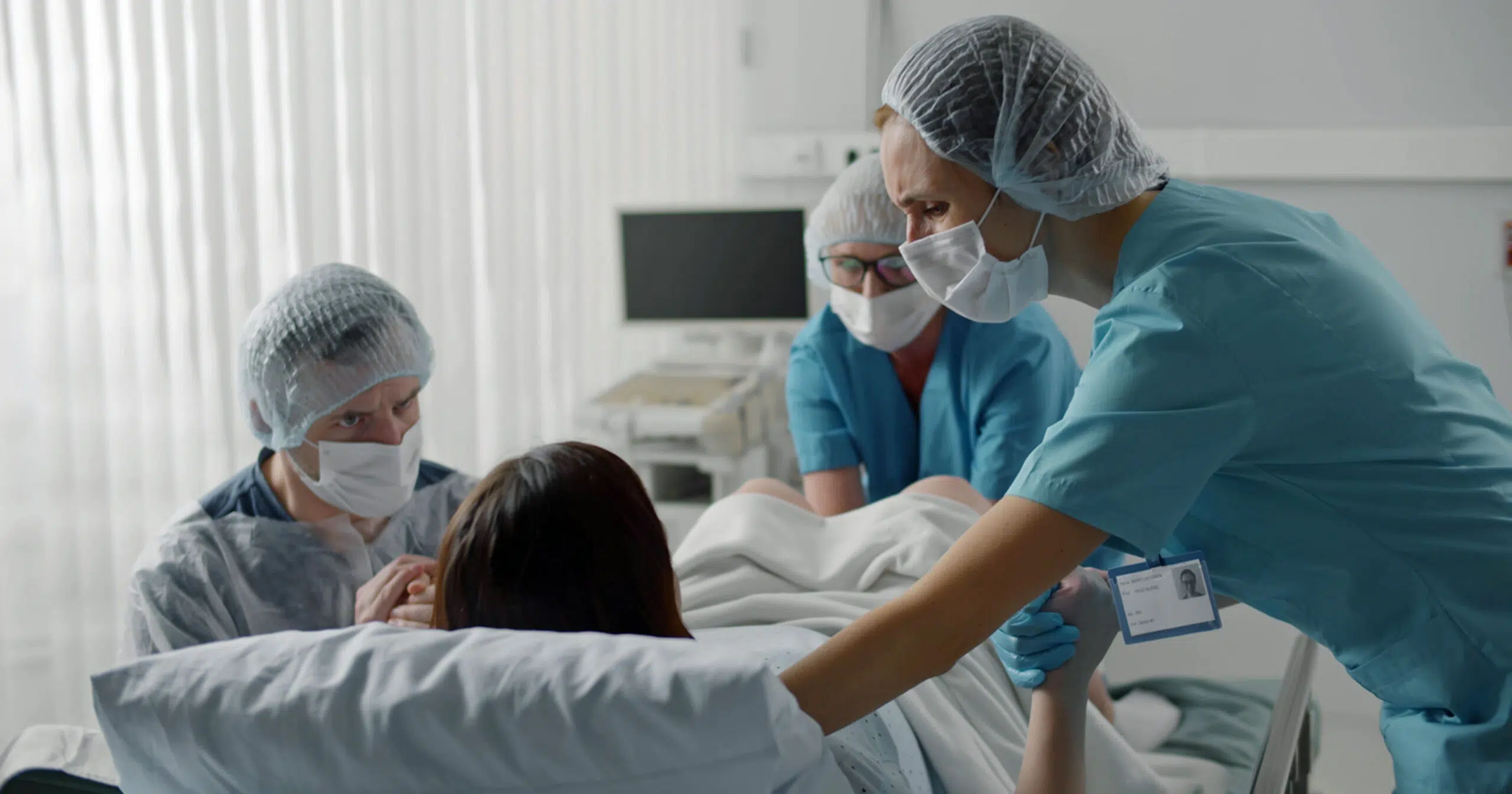

Obstetric nurses are vital in supporting women throughout their pregnancy, labor and childbirth, from prenatal assessments to labor support and postpartum care. Obstetric nurses advocate for the health and well-being of both mother and baby, empowering women to make informed decisions about their childbirth journey.
Recommended Certifications
- Obstetrics and Neonatal Quality and Safety
- Basic Life Support (BLS)
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS)
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS)
Transferable Skills and Knowledge
- Prenatal assessment
- Labor support
- Postpartum care
- Neonatal assessment
- Patient education
- Interdisciplinary collaboration
Transition Opportunities
- Postpartum Nurse: A background in obstetric assessment, labor support and neonatal care provides a solid start for this specialty, where nurses monitor maternal health, assist with breastfeeding, educate new mothers on newborn care and offer emotional support directly after childbirth.
- Neonatal Intensive Care Nurse: Leveraging expertise in neonatal assessment and care to provide specialized support to premature or critically ill newborns and their families is a natural transition.
- Lactation Consulting: With their understanding of maternal and newborn care, obstetric nurses can pursue roles as lactation consultants, offering breastfeeding support and education to new mothers and promoting successful breastfeeding experiences.
6. Operating Room Nurse: The Surgical Expert

As one of the highest-paying RN specialties, operating room (OR) nurses assist during surgical procedures by preparing operating rooms, sterilizing equipment and supporting surgeons. OR nurses also monitor patient vital signs, administer medications and ensure patient safety throughout the surgical process.
Recommended Certifications
Transferable Skills and Knowledge
- Surgical preparation and assistance
- Sterilization techniques
- Patient monitoring and vital signs management
- Medication administration
- Team collaboration and communication
Transition Opportunities
- Pre-Operation/Post-Anesthesia Care Nurse: OR nurses can leverage their surgical preparation and patient care expertise to excel in providing comprehensive perioperative care to surgical patients before and after procedures.
- Endoscopy Nurse: OR nurses bring procedural expertise and patient care skills to endoscopy roles, ensuring efficient and attentive care for patients undergoing endoscopic procedures.
- Outpatient Surgery Centers: Transitioning to outpatient surgery centers allows OR nurses to apply their knowledge in preoperative assessment and patient education, supporting patients undergoing minor surgical procedures in a convenient setting.
7. Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing: The Behavioral Health Specialist
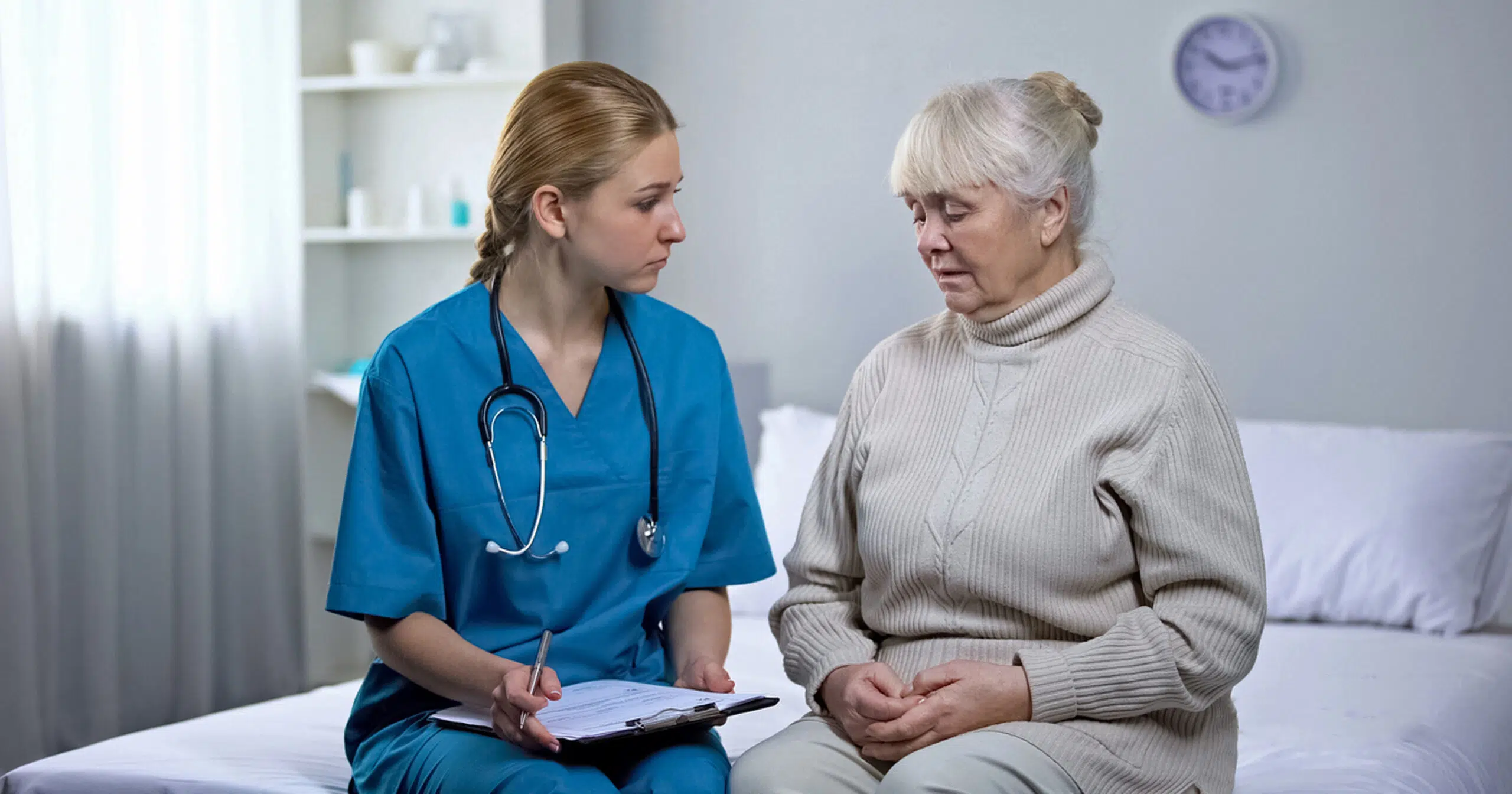

Psychiatric nursing involves caring for individuals with mental health disorders, offering support, therapy and medication administration. Nurses in this specialty work with patients closely to manage symptoms, promote wellness and facilitate recovery. Psychiatric nurses play a crucial role in advocating for mental health awareness and reducing the stigma surrounding mental illness.
Recommended Certifications
Transferable Skills and Knowledge
- Therapeutic communication
- Psychosocial assessment
- Crisis intervention and de-escalation techniques
- Medication and behavioral management
- Patient advocacy
- Collaboration with multidisciplinary teams
- Mental health education
- Treatment planning
Transition Opportunities
- Clinical Liaison Nurse: Psychiatric nurses use their expertise in communication, crisis intervention, treatment planning and patient advocacy to make great clinical liaisons, where they can bridge gaps in healthcare delivery and promote holistic outcomes.
- Addiction Medicine Nurse: With their understanding of mental health conditions and behavioral interventions, psychiatric nurses can transition into addiction nursing, where they assist individuals struggling with substance abuse disorders.
- Correctional Nurse: Psychiatric nurses transitioning to corrections nursing use transferable skills to de-escalate tensions, provide compassionate trauma-informed care and empower inmates through education. These abilities enable psychiatric nurses to seamlessly contribute to corrections healthcare, positively impacting inmate mental health.
Strategies for Transitioning Between RN Specialties
Prioritize continuing education, certifications and networking opportunities to enhance your skills and knowledge in the new field and ensure a smooth transition. Embrace soft skills such as adaptability, effective communication and a commitment to lifelong learning, which are essential for success in any nursing role.
Take the time to reflect on your reasons for wanting to change specialties and consider shadowing a nurse already working in the field to gain valuable insight and perspective. By taking these proactive steps and carefully considering your motivations, you can confidently navigate your transition and set yourself up for success in your new nursing specialty.
Embracing flexibility in nursing opens many opportunities for personal and professional growth. Exploring various specialties and roles in nursing helps prevent burnout, enables career advancement and promotes higher staff salaries or travel salaries. By diversifying their skill set and experience, nurses can find fulfillment in their careers while making meaningful contributions to healthcare.
Download the Vivian app for the latest job alerts in the specialty of your choice. Your dream nursing job is just a click away.









